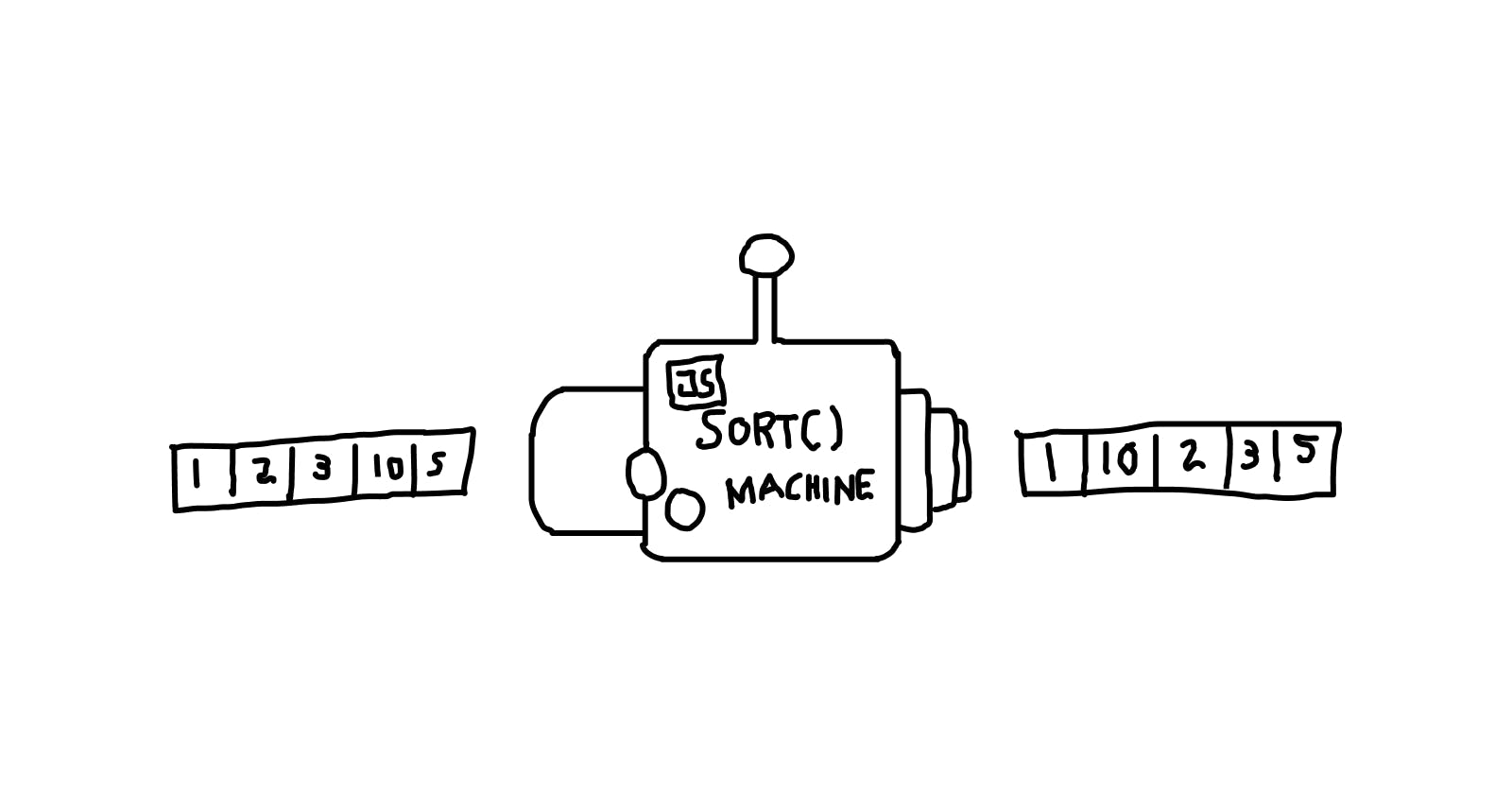
When sorting an array, if you are like me the first thing that comes to mind is sort().
An hour before writing this, I was having a great Sunday and decided to do some of the easy katas in codewars. One of the questions I found required me to add one line of code to sort an integer array, easy right?

The sort() method sorts the elements of an array in place and returns the sorted array. By default, the sort() method sorts the elements in ascending order according to the Unicode values of the elements.
// input: [1, 2, 3, 10, 5]
function sortArr(input) {
return input.sort()
}
// output: [1, 10, 2, 3, 5]
// 😡 expect output: [1, 2, 3, 5, 10]
So this got me 😡 but then if we are to go back and re-read how the sort method works, it by default sorts the elements in ascending order according to the Unicode values of the elements with Unicode values being highlighted.
So what is happening here:
The sort() method converts the numbers to strings and sorts them lexicographically (dictionary order) based on their string representations.
The Unicode code points for the characters "10" and "2" are:
"1": U+0031
"0": U+0030
"2": U+0032
In the string "10", the character "1" has a lower Unicode code point than the character "2", which means that in lexicographic order, "10" comes before "2". This is why the sort() method sorts the array [1,2,3,10,5] as [1,10,2,3,5].
But we are not doomed,
that's how sort() works by default, but you can provide a function to the sort() (I guess that would make it the sorting function) to specify a custom sort order. so to sort elements in ascending order by their numerical values add this function.
// input: [1, 2, 3, 10, 5]
function sortArr(input) {
return input.sort((a,b) => a - b)
}
//😃 output: [1, 2, 3, 5, 10]
In this example, the sorting function (a, b) => a - b subtracts b from a, so if a is less than b, the result is negative and a is sorted before b. If a is greater than b, the result is positive and b is sorted before a. If a and b are equal, the result is 0 and their order in the sorted array is unchanged.
You are sorted now, take that, elements :)